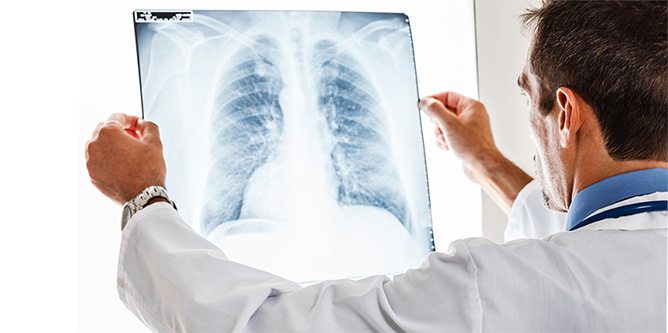
Lung infection is a type of infection which may develop in the lower respiratory tracts due to various causes. Primary cause is viruses and bacteria accumulating and proliferating in the lung tissue. It mostly develops following an infectious disease such as flu. It causes dyspnea by leading to pulmonary inflammation and increase in mucous production. Main symptoms are high fever, phlegmy coughing, breathing noisily and chest pain. Mild infections can spontaneously heal with good care. In some cases, it may be necessary to administer antibiotics or antiviral medicines. Hospitalization may be required for further treatments in severe infections. Little children, the elderly, those with chronic diseases, and smokers with weak immune system are at higher risk.
Table of Contents
What is lung (pulmonary) infection?
Lung infection is a type of microbial infection that affects alveoli or the bronchi connecting the lungs to the respiratory tract. It causes excessive sputum and inflammation, thereby making it difficult to breathe through airways. Most infections can be pulled through slightly, but some are serious and can be fatal. The most common types are acute bronchitis and pneumonia. It is mostly seen in winter.
Lung infections can affect everybody. It should be taken seriously and medications should not be quitted in the treatment process without the approval of your doctor. It can be fatal if a treatment is delayed or interrupted. (1)
Causes of lung infection
It is usually caused by a bacteria or virus that accumulates in the lungs and proliferates. It is more common in winter following cold or flu. As respiratory droplets carry the infection, it can be transmitted to someone else through coughing or sneezing.
The microbes that hang in the air for a while may fall down to surfaces and anyone touching these surfaces may also touch other things and spread the microbes further. This infection can also be caused by fungi, though rare.
There is a higher risk of developing pulmonary infection in those with weak immune system and pregnant women.
Types of lung infections
There are 3 types of pulmonary infections depending on where they develop:
Acute bronchitis
It can be caused by a virus or bacteria. However, viral bronchitis is more common. It is mostly caused by viruses leading to flu and cold. The bronchial tubes carrying air into the lungs get inflamed.
Fever and phlegmy cough are typical symptoms. It can also cause sore throat and nasal congestion. It can be seen in any age group. It usually heals spontaneously. (2)
Bronchiolitis
It is a viral infection which develops in bronchiolitis, the smallest airways in the body. It develops more frequently in children and babies under two years old. It can heal spontaneously with good care. However, in cases such as dyspnea and feeding disorder, it may require hospitalization. (3)
Pneumonia
It is mostly caused by bacterial infections. Sometimes, it can also develop due to viruses or fungi. As a result of the infection, alveoli are inflamed and filled with pus or fluid. As a result, it becomes difficult for oxygen to be transferred to other organs via the bloodstream.
Its symptoms are similar to those of acute bronchitis, but can suddenly exacerbate within 24-48 hours. In this case, emergency intervention is required. If left untreated, it can develop deadly complications such as pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura), lung abscess and septicemia (blood poisoning).
Fungal pneumonia is rare. It often affects people who take antibiotics frequently or have weak immune system. (4)
Symptoms of pulmonary infection
- Chronic cough
- Yellow or green-coloured dense sputum (sometimes with blood)
- Dyspnea or tachypnea
- Breathing noisily
- High fever
- Perspiration
- Headache
- Fatigue and dizziness
- Sharp chest pain while coughing or taking a deep breath
- Tachycardia
- Loss of appetite
- Myalgia and/or arthralgia intensely on the back
Mild pulmonary infections, such as acute bronchitis, can heal spontaneously with good care at home in 7-10 days. However, if it lasts longer in people with weak immune system, the severity and danger of the infection may increase and turn into pneumonia.
If you have difficulty in breathing, with high fever, or feel worse consult your doctor or go to the emergency immediately.
Diagnosis of lung infection
Doctors ask patients about their symptoms, general state of health, and medical history. Doctor can diagnose by taking patients’ temperature and listening to their lungs using a stethoscope. Sometimes tests such as chest x-ray, breath tests, and sputum or blood samples may be needed to determine the level of the progression of infection.
Treatment of lung (pulmonary) infection
Main treatment for advanced pulmonary infections is medicines. Medicines that stop the development of pulmonary infection and thus inflammation based on the type of infection are: (5)
- Antibiotics: They can be administered only for bacterial and severe infections. It should be taken at the recommended doses until the end of dosage. Unconscious use may lead to antibiotic resistance, i.e. drug inefficacy in severe infections.
- Antivirals: May be required in severe viral infections developing in the lungs.
- Antifungals: They are used in fungal lung infections.
In addition, painkillers, antipyretics, antitussives and expectorants, and bronchodilators can be used to relieve symptoms while the body is fighting infection.
In more serious infections, hospitalization may be required. Main treatments administered in hospitals are:
- Ventilatory support
- Intravenous aggressive antibiotic treatment
- Serum liquid supplement due to sever dehydration
Recurring lung infection
Infection heals spontaneously in healthy people and those with strong immune system and does not mostly recur. However, some factor may lead to the recurrence of an infection. Main factors are as follows: (6)
- Antibiotics treatment which is discontinued
- Diseases such as chronic bronchitis, CORD, cystic fibrosis, asthma causing inflammation which damages the lung tissue and is not microbial.
- Undeveloped immune system (especially babies and children at the age of <5)
- Old age
- Cancer and chemotherapy
- Weakened immune system due to HIV/AIDS or transplantation
- Smoking habit and alcoholism
These people should get flu vaccine every year and a pneumonia vaccine every 5 years. In particular, recurring infections may lead to pneumonia. The disease ranks first among infection-related deaths.
Herbal medicine for lung infection
- Tussilago farfara: It is good for acute bronchitis as it can remove inflammation in the bronchi. It softens sputum, facilitates its removal through coughing and loosens up the chest. You can drink 3 cups of brewed tea daily.
- Inula Helenium root: It is especially effective in bacterial pulmonary infections. It can relieve symptoms such as fever and phlegmy cough. You can boil it in a coffee pot for 5 minutes and drink 1 dessertspoon 3 times a day. It is also beneficial to drink 1 tablespoon of inula helenium molasses on an empty stomach in the morning.
- Garlic and onion: Both are highly effective natural antibiotics in the treatment of pulmonary infections. They have an anti-inflammatory effect. You can boil 1 clove of garlic or 1 shallot in a coffee pot and drink 1 cup every day. Honey and lemon can be added to the mixture.
- Natural honey: Drinking 1 dessertspoon of honey and half a lemon mixed in warm water will help loosen up the chest. You can also get an effective syrup mixing some spices, which have antibacterial effects, with honey. Herein, squeeze 1 tablespoon of honey, 1 dessertspoon of ginger, turmeric, black pepper and 1 lemon into a jar of water and shake well. If you drink 1 dessertspoon 3 times a day, it will allow you to breathe more easily by removing the sputum.
Herbs are used for supportive treatment. However, they should not be used without consulting a doctor as they may cause side effects in some people.
Prevention of lung infection
The most effective ways to prevent pulmonary infections are:
- Get a vaccine: Those who have higher risk especially to develop this infection can get flu and pneumonia vaccines on a regular basis.
- Quit smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and weakens the body against infections. Also stay away from excessive and long-term use of alcohol.
- Consider hygiene: Cover your mouth while coughing or sneezing and wash your hand regularly. Throw used paper napkins away immediately.
- Eat healthily and properly: Follow a diet which will help strengthen your immune system. Balance vitamin, mineral, protein and carbonhydrate intake in your meals. Stay away from excessively oily,high-sugar and processed foods.
Recommendations for lung infection
- Drink plenty of water (help soften sputum and cough easily).
- Drink warm liquids containing honey and lemon. It could be herbal teas, such as linden and echinacea.
- Eat foods with high water content such as red lentil soup with bone broth or chicken broth soup, which are high in vitamin and protein, and eat plenty of fruits containing vitamin C.
- If the infection causes sore throat, gargle with warm saline solution (do not let children try).
- Rest until you feel good.
- Use a few pillows to keep your head high (makes breathing easier).
- Ventilate your room to freshen the air.
- Keep the air in the room humid or breathe steam from a bowl of hot water. Vapor inhalation method should not be used in children due to the risk of scalding.
- If your symptoms last long and get worse, see your doctor immediately.