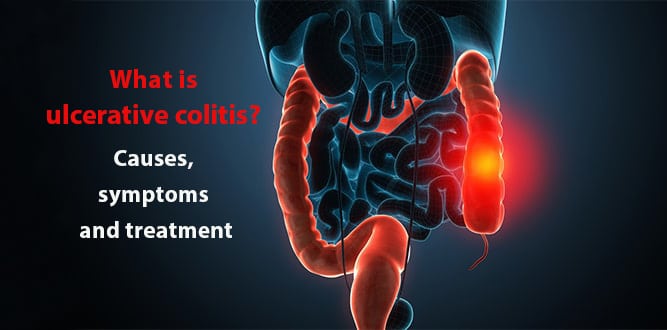
Ulcerative colitis is an inflammatory disease of the digestive tract that damages the large intestine. It can lead to repeated diarrhea, bloody feces, abdominal pain, extreme fatigue, decreased appetite and weight loss. The course of the disease proceeds with occasional exacerbations and silent periods. Ulcerative colitis can affect people of all ages, but is usually diagnosed between 15-25 years of age. It is equally found among women and men. There is no definitive treatment. The preferred treatment, which aims at reducing inflammation, is drug therapy. Surgical intervention is more rare.
Table of Contents
What is ulcerative colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is an intestinal disease that causes long-term inflammation and ulcers in digestive tract. It affects the mucosa covering inner side of large intestine (colon) and the rectum. Ulcerative colitis can lead to complications that cause the body to degrade and can even cause death. Symptoms usually develop over time and vary depending on location and severity of the disease.
Types of ulcerative colitis
- Ulcerative proctitis: This is the lightest form of ulcerative colitis. Inflammation is limited to closest area to the anus (rectum) and manifests itself with rectal bleeding.
- Proctosigmoiditis: Only the last part of large intestine (rectum and colon) is involved. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal cramps, pain and failure to defecate.
- Left sided colitis: Inflammation extends to left side of the colon up to the spleen. It is manifested by bloody diarrhea, weight loss, abdominal cramping and pain on left side.
- Pancolitis: Pancolitis often affects all the large intestine, and can cause severe diarrhea, bleeding, abdominal cramps, pain, fatigue and significant weight loss.
- Acute severe ulcerative colitis: This rare form of colitis affects the entire colon, and causes severe pain, diarrhea, bleeding, fever and ingestion failure.
Causes of ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is considered to be an autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system, which is the body’s defense system, attacks healthy tissues. Although it is not known what causes the immune system to behave in this way, most experts believe it is the result of a consolidated effect of genetic and environmental factors.

Symptoms of ulcerative colitis
- Recurrent diarrhea may be seen with bloody, mucous feces.
- Abdominal pain
- Exhaustion
- Fever
- Decreased appetite
- Frequent defecation needs
- Anemia
Less often seen:
- Joint pain
- Eye Irritation
- Rashes
Diagnosis of ulcerative colitis
Your doctor will examine you after he/she hears your health history. If necessary, the following tests may be required:
- Blood tests: They help to determine if there is a condition of anemia or inflammation.
- Stool sample tests: It can help doctor to rule out any infection or parasite in colon.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy: A flexible tube with light and camera at the tip is placed through the rectum area to look at the bottom of the column. During this procedure, biopsy can be performed after a small piece is taken from the lower colon.
- Colonoscopy: It is the same procedure as flexible sigmoidoscopy, but colonoscopy looks at the entire colon. A blue dye can be sprayed during the procedure onto the column to see which parts are affected by ulcerative colitis. This is called chromoendoscopy.
Treatment of ulcerative colitis
The choice of treatment is based on degree of disease activity, development of the disease, the frequency of relapses, symptoms outside the intestine, previous medications, side effects of drugs and the preference of patient.
Ulcerative colitis medications
The aim of medications in ulcerative colitis is to prevent/suppress the inflammatory activity of the colon mucosa and to put the disease into a silent period. Depending on the severity of the disease, one or many drugs may be preferred.
- Corticosteroids: In the active period of acute ulcerative colitis, corticosteroid drugs can be administered, reducing inflammation and fever, relieving abdominal pain, decreasing diarrhea and improving appetite. Locally effective, Budenofalk capsules (budesonide) have fewer side effects.
- Corticosteroid clyster and foams: These drugs relieve problems in the rectum.
- Sulfasalazine: Its sulfapyridine content may cause skin rash, headache, stomach pains, nausea and anemia in some patients. It sometimes prevents fertility in males as it reduces sperm count. However, this is a temporary situation.
- 5-ASA group drugs: Less side effects, but still diarrhea, headaches and skin rashes.
- Azathioprine: Drugs such as azathioprine, which affect the immune system, prevent the activation of the disease in the long term. The drug is started at low doses; the dose is gradually increased, then it can be monitored if side effects may occur. White blood cell counts should be performed intermittently when using this group of drugs.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics such as metronidazole or ciprofloxacin may be used in the treatment of conditions such as inflammation and abscess around the anus.
- Vitamin supplements: In patients with anemia, vitamin and mineral supplements such as iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 may be needed.
Ulcerative colitis surgery (colectomy)
Ulcerative colitis surgery, also known as colectomy, involves taking all or a part of the large intestine. The small intestine is connected to the anus to discharge the waste from the body instead of the large intestine. Conditions requiring surgery in ulcerative colitis:
- Intensive bleeding
- Hazardous or punctured toxic megacolon
- Severe acute ulcerative colitis not responding to steroid therapy
- Intestinal obstruction due to stricture
- Suspicion of colon cancer
- Untreatable conditions due to the development of systemic complications in drug treatments
- Failure to control the disease
- Developmental retardation in pediatric patients
Surgical procedures in ulcerative colitis is depending on severity of the disease:
Subtotal colectomy with Ileostomy
Subtotal colectomy is the most common surgical method in the treatment of ulcerative colitis and usually allows the pouch surgery to be performed at a later date. During this procedure, surgeon removes the colon, but leaves the rectum. Then he/she opens a hole into the abdominal wall and connects this hole to the end of the small intestine.
This operation is called ileostomy or stoma. Special bags are placed on this hole for the collection of post-operative wastes. In subtotal colectomy, ileostomy can be temporary or permanent. Depending on the patient’s condition, the end of the small intestine can then be placed in the anus.
Restorative Proctocolectomy with ileo-anal pouch
This procedure is usually referred to as pouch surgery. This procedure requires two or three operations. In the first operation, the surgeon removes the entire colon, but leaves the rectum and the anus. As with subtotal colectomy, a temporary ileostomy is done to collect waste from digestion. At this stage, patients usually quit their ulcerative colitis drugs. During the second operation, the lower end of the small intestine is connected to the anus in order to form a pouch.
The pouch aims to alter the function of the rectum and stores the stool until it is discharged from the body. Ileostomy usually gives this pouch a recovery period of three months. This temporary ileostomy can then be closed in the second or third operation.
The advantage of this surgery is that you can pass stools. Because a pouch cannot fully perform the function of a healthy colon, many people may experience intestinal activation 6 to 8 times a day.
Total colectomy
In this operation, the large intestine is removed including the rectum up to the anal canal. Once the large intestine is removed, intestinal continuity should be ensured. Therefore, the small intestine is connected to the abdomen by opening a hole. Special bags are placed on this hole for the collection of post-operative wastes. Although this operation is non-reversible, there is no risk of developing inflammation or bowel cancer.
Laparoscopy
Some of the procedures above can be performed by laparoscopic surgery. Instead of making a big hole in the abdominal wall, the surgeon makes four or five small incisions, each of which is only about 1 cm long. Small tubes are passed through incisions and a harmless gas is given to inflate abdomen a little bit to create more space for the surgeon.
A thin tube with light and camera on the tip called laparoscope examines the abdomen. Laparoscopic operations take longer than open surgery, but have advantages such as less pain, smaller surgical scars, and rapid recovery.
Herbal treatment of ulcerative colitis
There is no definitive herbal treatment of ulcerative colitis, but some studies have shown that some plants provide relief in symptoms. You should consult your doctor before attempting any herbal treatment for your illness. Some recommended plants are:
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera is a tropical plant used in traditional medicine throughout the world. Studies have shown that the anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera gel are beneficial in the inflammation of ulcerative colitis.
- Boswellia serrata: Ayurvedic medecine obtained from resin and traditionally used for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. In a study with animals, Boswellia was found to reduce chemical edema and inflammation in the intestine.
- Licorice root: This herb is a plant widely used for various diseases. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate is a purified substance derived from licorice root and has been found to improve intestinal mucosal inflammation.
- Wheatgrass: A study has shown that wheatgrass water can be safely used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
- Turmeric: Its anti-inflammatory activity is known. It helps to break up fatty cells by supporting bile flow. In addition, it reduces gastric acid secretion and provides protection against digestive system ulcers. In a study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology in August 2015, turmeric was found effective in creating remission in patients with active, mild to moderate ulcerative colitis.
Diet for ulcerative colitis
In ulcerative colitis, some nutrients worsen symptoms in some people. Frequent and small amounts of food can help you control the symptoms. Low-fiber foods during the exacerbation of the disease may sometimes contribute to the alleviation of symptoms. For example:
- White bread
- White rice, refined pasta
- Cooked vegetables
- Lean meat and fish
- Eggs
Because your body will lose liquid due to diarrhea, you should drink plenty of water. By consulting your physician, it may be beneficial to take minerals and vitamins such as iron and calcium.
Does Ulcerative colitis kill?
The mortality rate is higher in elderly patients and patients with complications such as malnutrition and anemia. The most common cause of death in ulcerative colitis patients is toxic megacolon.
Ulcerative colitis and cancer
The risk of developing bowel cancer is higher in patients with ulcerative colitis. Since abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea, which are symptoms of bowel cancer, are also seen in ulcerative colitis, patients are often unaware of the situation. Therefore, it is usually helpful to have a colonoscopy done 10 years after the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. In addition, the use of aminosalicylated drugs reduces the risk of cancer development.
Recommendations for ulcerative colitis patients
- Although stress does not cause ulcerative colitis, reducing stress may reduce the frequency of attacks.
- You should stay away from beverages with a large amount of caffeine (coffee, tea, chocolate).
- The risk of developing osteoporosis increases in patients with ulcerative colitis. This condition is not directly caused by the disease, but is due to the use of long-term drugs containing cortisone.
- Most women with ulcerative colitis can have a normal pregnancy and have a healthy baby. However, in the event of conception during the exacerbation period of the disease, the risk of premature birth and having a low weighted baby may increase.