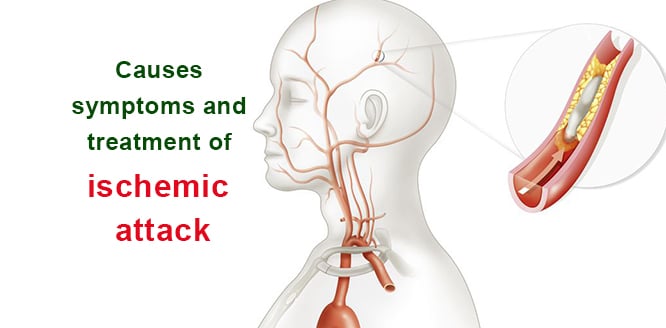
Ischemia is a serious condition in which blood flow to any tissue or organ in the body is reduced or stopped. During ischemia, one of the blood vessels providing blood and oxygen to the brain, is blocked. This congestion can be caused by blood clots, plaques or air bubbles. Interruption in blood flow prevents the function of organs. Therefore; may cause life-threatening problems such as heart attacks or strokes and symptoms such as speech difficulties, confusion, weakness in arms and legs. Smoking, excessive alcohol, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, obesity, diabetes and old age are the most important risk factors. People over 60 are more at the high risk.
Table of Contents
What is Ischemia?
Myocardial ischemia occurs when blood flow to your heart is reduced, preventing it from receiving enough oxygen. The reduced blood flow is usually the result of a partial or complete blockage of your heart’s arteries (coronary arteries). The brain, heart, legs and intestines can be affected.
The symptoms and treatment vary depending on the place where it occurs and the affected area of the brain. Transient ischemic attack is associated with loss of brain function in a restricted region, resulting in alarming clinical symptoms.
Causes of ischemia
- Coronary artery disease and Atherosclerosis: Plaques made up mostly of cholesterol build up on your artery walls and restrict blood flow. Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of myocardial ischemia.
- Blood clot: The plaques that develop in atherosclerosis can rupture, causing a blood clot. The clot might block an artery and lead to sudden, severe myocardial ischemia, resulting in a heart attack. Rarely, a blood clot might travel to the coronary artery from elsewhere in the body.
- Coronary artery spasm: This temporary tightening of the muscles in the artery wall can briefly decrease or even prevent blood flow to part of the heart muscle. Coronary artery spasm is an uncommon cause of myocardial ischemia.
Ischemia types
Myocardial ischemia
It is a condition where blood flow to one or more coronary arteries in the heart decreases and does not receive sufficient oxygen. Myocardial ischemia, also known as heart ischemia, can damage the heart muscle and reduce the ability to pump.
This sudden obstruction can lead to irregular heartbeat, heart failure and even heart attack, resulting in chest pain and sudden cardiac death. Symptoms usually go through rest or relaxation but are a medical emergency.
Myocardial ischemia risk factors
- Tobacco use
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure, cholesterol
- High blood triglyceride level
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
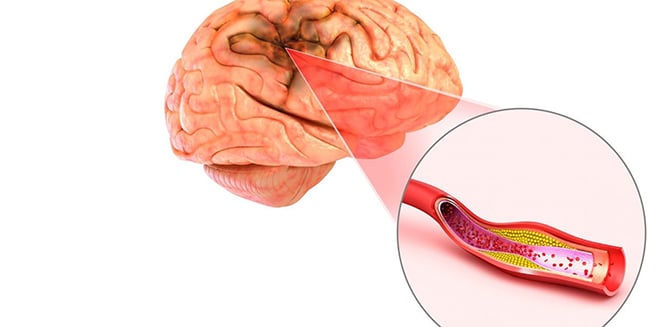
Brain ischemia
Brain tissue is metabolically very active, and in order to function properly, the brain receives 20 percent of the blood pumped by the heart. Furthermore, brain has no energy stores of its own and is completely dependent on continuous blood flow to do its work.
Consequently, brain tissue rapidly becomes ischemic if blood flow is interrupted, and unless the blood flow is rapidly restored brain death quickly ensues.
The death of brain tissue is called stroke. Sometimes the blood flow is not long enough to produce an actual stroke. This condition is called a “transient ischemic attack” (TIA). TIAs are important not only because they are alarming in themselves, but also because they are often followed by a full stroke. Thus, TIAs always require immediate medical attention.
Critical limb ischemia (Extremity ischemia)
It is a serious condition that occurs with plaque accumulated in arteries in the legs and can cause permanent disability if left untreated. The first sign of peripheral arterial disease arises from the hardening of the arteries that provide blood to the legs.
The most common symptom of limb ischemia, which may cause intense pain even when resting, is intermittent limping.
Signs of critical limb ischemia
- Coldness and weakness in the legs
- Pain in feet
- Bright, smooth skin on legs and feet
- Nonhealing wounds
Mesenteric ischemia (Intestinal ischemia)
Chronic intestinal ischemia, which is usually produced by atherosclerosis of the intestinal arteries, typically causes recurrent symptoms after a meal, when the intestines are trying to perform their digestive work in the face of an insufficient blood supply. Acute intestinal ischemia may occur when an embolism (blood clot) lodges in the intestinal arteries. If the embolism is severe, intestinal infarction, which is a medical emergency, may occur.
Symptoms of mesenteric ischemia
- Abdominal pain, swelling after each meal
- Blood in the stool, diarrhea
- Pressure in the intestines
- Nausea
Symptoms of Ischemia
- Single eye blindness or double vision
- Depending on the affected artery, weakening or paralysis in leg on one side of body.
- Dizziness, vertigo
- Confusion in the mind
- Loss of coordination
- Inability to move one side of the face
These symptoms are common symptoms of ischemia.
Signs of ischemia in the heart
- Chest pain
- Neck, jaw, shoulder or arm pain
- Fast heart rate
- Shortness of breath when exercising
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sweating
- Fatigue
If you have prolonged or severe chest pain, seek immediate help.
Ischemia symptoms in the brain
- Strong and fast relapsing headaches with dizziness or vomiting
- Passing out
- Problems in moving the body (unable to move the face, arm or leg on one side of the body, weakness, numbness)
- Slurred speech and difficulty in understanding others
Ischemia may persist for a short time and recover on its own, but intervention as quickly as possible is essential to avoid unreversible damage.
How does ischemia affect the body? What are the causalities?
Transient ischemic attack is a warning sign that you may be at risk of a stroke in the near future. Detailed medical evaluation is the best way to reduce this risk.
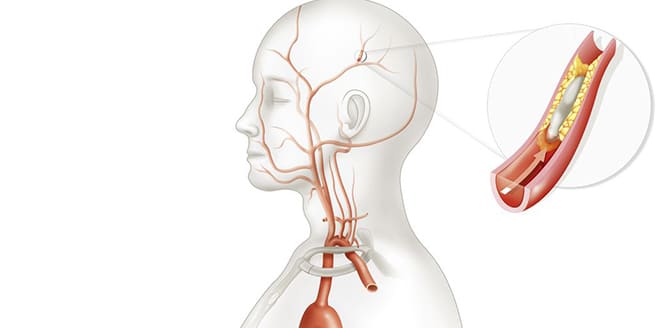
If left untreated, it can lead to serious damage to cells and tissues, can lead to serious complications, such as organ death, irregular heart rhythm (arrhythmia), heart failure, heart attack, cerebral hemorrhage, stroke, bowel obstruction.
Diagnosis of ischemia
Rapid diagnosis of symptoms is vital to diagnose the cause of ischemia and to decide on the treatment method. Tests for evaluating ischemia include:
- Complete blood count, fasting glucose levels
- Tests showing brain and blood vessels such as cardiac CT scan, angiography (CCTA), MRI, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), angiogram, arteriography and nuclear scan.
- Carotid Doppler ultrasonography to monitor blood flow
- Echocardiogram (ECO)
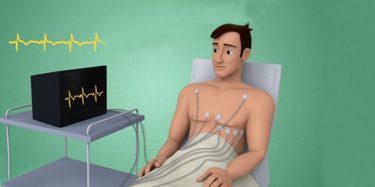
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Treatment of ischemia
Treatment depends on personal circumstances such as age and medical history. The first target in the treatment is to regulate the breathing by normalizing the heart rate and blood pressure. Depending on the severity of your condition, you may be treated with medications, surgery or both.
Medications
- Long term treatments include aspirin or anticoagulants.
- Thrombolytic drugs: One of the main therapies is intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). It is more effective if given within 4.5 hours of stroke onset. Patients who have had hemorrhagic stroke, brain hemorrhage, or head trauma may not be given tPA as it may result in bleeding; in this case, clots can be removed by surgery.
Surgical treatment
- Carotid endarterectomy: It is surgery that removes plaque buildup from inside a carotid artery in your neck.
- Angioplasty (stenting): A long, thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the narrowed part of your artery to open it.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery: This type of open-heart surgery is usually used only for people who have several narrowed coronary arteries.
Ischemic stroke and ischemic attack
Ischemic stroke is caused by a blockage due to the accumulation of fat and clot in an artery that supplies blood and oxygen to the brain. Requires rapid treatment; If not treated immediately, blood flow remains blocked, causing brain damage or death. If you think someone has had a stroke, consider the situation with the following in mind:
- Does one side of the face droop?
- Does one arm drift downward when arms are raised?
- Is there any slurred or strangeness in speech?
If the answer to these questions is yes, seek medical attention without wasting any time.
Rehabilitation may be required to regain motor skills and coordination after treatment. Professional, physical, and speech therapy help to restore other lost functions. If you still have a problem after a year, it will probably be permanent. Global ischemia, a more severe form of stroke, occurs when the oxygen flow to the brain stops completely.
It is usually caused by a heart attack, but other conditions such as carbon monoxide poisoning may also be the cause.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA): it is like a stroke that produces similar symptoms but lasts only a few minutes and does not cause permanent damage. Ischemic attack, also called mini-stroke, is temporary but a warning; increases the risk of future stroke. It is caused by a temporary congestion in the brain or a decreased blood flow. The deterioration in the blood supply results in a lack of oxygen in the brain.
It may cause sudden symptoms like stroke and visual impairment; drowsiness or weakness in the face, arms and legs. After a short time, the symptoms disappear and the blood flow returns to normal.
Causes of ischemic attack
Blood clots that prevent blood flow are the most common cause of ischemic stroke and attacks. Blood clots can be the result of arteriosclerosis, heart attack or abnormal heart rhythms. The brain cells are affected within seconds after obstruction and cause severe symptoms in the regions controlled by these cells. Circulatory conditions are the main risk factor for ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack:
- Atherosclerosis
- Atrial fibrillation (cardiac arrhythmia)
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Having a heart attack, attack or stroke
- Sickle cell anemia
- Coagulation disorders
- Congenital heart defects
- Carotid artery disease
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- High levels of homocysteine (high levels of this amino acid in the blood can cause arteries to thicken)
Other reasons include
- Diabetes
- Family history
- Gender (the risk is more in men)
- Old age (risk increases after age 55)
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Physical inactivity
- Insufficient feeding
- Use of a contraceptives
- Obesity
- Drug use
Rare causes
- Bacteria, tumor cells or air bubbles that move throughout the bloodstream
- Inflammation of blood vessels caused by inflammatory diseases such as syphilis, tuberculosis
- Head or neck injury
- Tearing a blood vessel wall in the neck
Signs of ischemic attack
- Generally, weakness, drowsiness or paralysis on one side of the face, arm or leg
- Difficult to understand others and speech disorder
- Sudden blindness or blurred vision
- Dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Sudden and severe headaches
- Dysphagia (dysphagia)
Transient ischemic attack symptoms are similar to stroke and may start suddenly. Rapid assessment of treatable conditions can help prevent paralysis. If symptoms persist for more than an hour, there is a risk of stroke.
Ischemia and infarction
An organ exposed to ischemia is called ischemic. The ischemic organ starts to deteriorate as it does not get the oxygen and nutrients it needs, and this often causes symptoms. If ischemia becomes severe or lasts longer, the cells of the affected organ may begin to die. The death of all or part of the ischemic organ is called infarction.
The hardening of the arteries affects the blood vessels in the body, including arteries supplying blood to the heart and brain. Atherosclerosis affecting the blood vessels in the heart may cause chest pain or heart attack.
Ischemia prevention methods
After having an ischemic attack, it is more likely that another attack will recur. Knowing risk factors and acquiring a healthy lifestyle is the best thing you can do to prevent ischemia.
- Have regular medical examinations
- Do not smoke, limit alcohol intake
- Limit salt use
- Regular exercise; at least 30 minutes’ walk several days a week.
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Drugs such as cocaine increase the risk of transient ischemic attack or stroke
- Keep your blood glucose level in the target range; control of other health problems such as diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Always use the medication prescribed by your doctor
- Eat food that protects the heart; eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, high fiber foods, whole grains and fish at least 2 times a week. Choose fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids such as salmon, mackerel, trout, herring and sardines.
- Try breathing techniques, meditation and yoga to reduce your stress.
- Avoid too much fatty and salty foods. For more:>>> Ischemic Stroke