Acromegaly is a rare disorder caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone. Excessive hormone secretion of the pituitary gland leads to the tumor. This tumor causes overgrowth in various organs of body, especially in the bone structure, especially in hands, feet and face. Acromegaly can affect the bones and heart negatively, as well as triggering many diseases. It is usually seen in middle-aged people, but is likely to occur in children. Acromegaly may cause effects such as menstrual irregularity. The main treatment of acromegaly is surgery, but medication and radiotherapy also support treatment. Patients’ lifespan may vary but late diagnosis may lead to a significant reduction in lifespan. Early diagnosis is very important for treatment success.
Acromegaly is a rare disorder caused by excessive secretion of growth hormone. Excessive hormone secretion of the pituitary gland leads to the tumor. This tumor causes overgrowth in various organs of body, especially in the bone structure, especially in hands, feet and face. Acromegaly can affect the bones and heart negatively, as well as triggering many diseases. It is usually seen in middle-aged people, but is likely to occur in children. Acromegaly may cause effects such as menstrual irregularity. The main treatment of acromegaly is surgery, but medication and radiotherapy also support treatment. Patients’ lifespan may vary but late diagnosis may lead to a significant reduction in lifespan. Early diagnosis is very important for treatment success.
Table of Contents
What is acromegaly?
Acromegaly is a rare disease that causes the body tissues and hormones to grow faster than they should. Abnormal growths occur in the bone structure, especially in the hands and feet. In addition to this, abnormal growth in the eyebrows, nose, lips and tongue occurs. This disease can lead to severe joint pain, fatigue, sleep apnea, headache and impaired vision.
It can also cause irregularity of menstruation period in women and erectile dysfunction in men. Since it is a slowly progressing disease, it may not be noticed immediately. This can lead to a significant loss of time for the initial stage of treatment.
What causes acromegaly?
Acromegaly occurs when the pituitary gland produces excessive hormones that balance and regulate the physical development of the body. Most patients with acromegaly have a benign tumor that affects the pituitary gland. Although these tumors are common in many people, they may affect the person and cause them to catch this disease.
The growth of the pituitary gland may be the cause of environmental factors (air pollution, stress, radiation, etc.). In rare cases, a tumor in the lungs, pancreas, brain or other part of body may also cause acromegaly. Sometimes it passes through family, but most of time it is not hereditary. It is most common in middle-aged people, but might be seen at any age.
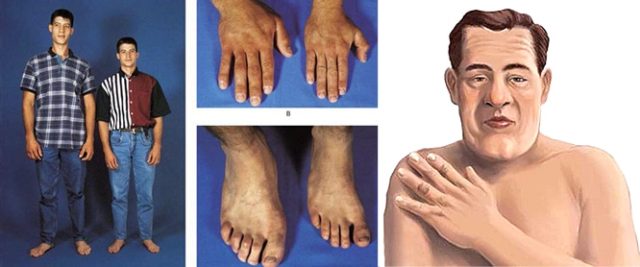
Acromegaly symptoms
- Abnormal growth of the face, foot and bones of the hand
- Excessive hair growth, especially in women
- Significant growth in chin, tongue, lips and eyebrows
- Excessive weight gain,
- Joint pain and swelling
- Significant diastema
- Aphonia
- Blurred vision,
- Fatigue-tiredness
- Headache,
- Sleeping problems,
- Muscle weakness,
- Excessive sweating
- Bad smell of the body,
- Blood in the stool,
- Oily skin,
- Irregular menstrual period,
- Erectile dysfunction
As the symptoms are usually slow, people may not realize the disease. If you notice one or more of these symptoms, necessarily go to a doctor.
Diagnosis of acromegaly
Since acromegaly is a slowly progressing disease, it can take a long time to diagnose. The patient’s history is important for diagnosis. Blood-glucose tests, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) and tomography (CT scan) may also be necessary for diagnosis of acromegaly.
- Blood-glucose test:The patient takes 75 to 100 grams of glucose and then gives a blood sample to determine the hormone level. If the body has normal levels of hormone, the given glucose will try to suppress this hormone level. Because glucose normally causes a decrease in hormone levels. The hormone levels in patients with acromegaly remain high since the body excessively produces hormones.
- MRI and Tomography:This test is useful for finding a tumor caused by excessive pituitary gland production. It is important to understand growth rate of bones.

Acromegaly treatment
The recommended treatment for acromegaly depends on symptoms you have. The aim is to reduce the growth hormone production to normal levels and to alleviate the effect of tumor on tissues. In the treatment of acromegaly, surgical intervention method has highest probability to achieve a definite solution. However, surgical operation may not be sufficient if the tumor is larger than expected. Then, radiotherapy, drug therapy or other methods are used.
Acromegaly surgery
The patient sleeps with general anesthesia. The surgeon makes a small incision under the nose or under the upper lip to reach the pituitary gland. Uses an endoscope to see the tumor. He then removes the tumor with the help of surgical instruments.
With the removal of the tumor from the body, the level of growth hormone decreases immediately as well as the pressure on the surrounding tissue. Usually the swelling will begin to descend within a few days and the face will get the normal appearance.
Acromegaly surgery risks
As with any surgical intervention, there are of course certain risks. There is a little chance of damaging the healthy parts of the pituitary gland during surgery yet, it is amongst the possibilities. It may also be possible that the fluid protecting the brain will leak out during the intervention. Meningitis is another rare risk. Ask your doctor about possible risks before going into surgery.
Acromegaly drug therapy
If there is no decrease in post-operative growth hormone level, drug treatment may be applied. If tumors are large, preoperative medication may be required to shrink them and reduce problems during general anesthesia.
Acromegaly drugs
- Bromocriptine (Parlodel)
- Cabergoline (Dostinex)
- Pegvisomant (Somavert)
- Octreotide (Sandostatin)
These drugs are used to regulate hormone levels. However, it can rarely cause gastro-intestinal disorders or elevated liver enzymes.
Radiotherapy
Radiation is used to destroy large tumors or parts of the tumor after surgery or when the drugs alone are not effective. It may be effective in lowering growth hormone levels when combined with the drug.
Radiation is performed in sessions at intervals of 4 to 6 weeks. It may take about a year to get results from this treatment. Radiation may have a negative effect on fertility. It can rarely cause vision loss, brain damage and secondary tumors.
Acromegaly herbal treatment
Some plants have therapeutic properties against metabolic diseases that acromegaly patients bear high risk to get. These are;
- Broccoli; it may be useful to consume to prevent colon cancer in particular.
- Black seed; good for many types of cancer.
- Cinnamon, almond and leek; especially diabetics can consume.
- Garlic; Strengthens heart health.
- Ginger, kiwi; It is important for the immune system.
- Onion, safflower, flaxseed; Good for cardiovascular diseases.
However, side effects may occur as a result of the interaction of some plants with some drugs. Thus, consult your doctor before using any plant.
What happens if acromegaly goes untreated?
Untreated acromegaly can cause serious health problems. These;
- Heart failure,
- Hypertension,
- Vision loss,
- Diabetes,
- Spinal cord compression,
- Goiter (thyroid gland growth),
- Uterine tumor,
- Nerve compressions (Carpal tunnel syndrome)
- Liver and spleen enlargement,
- Type 2 diabetes,
- Shortness of breath and breathing difficulty,
- Skin darkening in some parts of the body
Acromegaly can also cause the accumulation of fluid in the heart, lung and various body tissues.
Acromegaly and metabolic diseases
If acromegaly is not treated, it may trigger a number of metabolic diseases. These are;
- Arthritis (inflammation)
- Renal failure
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Diabetes
- Intestinal polyps
- polyps in the colon
- Respiratory diseases
- Cholesterol
How does acromegaly affect women?
Although the effects of acromegaly have similar characteristics in every individual, it affects women from different perspectives. The disease can cause menstrual cycle irregularity, excessive hairiness, and abnormal milk flow from the breast apart from the pregnancy or breast-feeding.
Life expectancy of acromegaly
There is no definite information in the medical literature about how long acromegaly patients can survive. However, patients’ life expectancy decreases by approximately 10 years. The risk of diabetes and heart disease is higher, especially in severe patients. This may decrease the life quality and decrease the life expectancy.
Acromegaly can cause fatal consequences if left untreated. However, early diagnosis positively affects treatment success.
Gigantism vs acromegaly
Gigantism is a disease caused by the non-cancerous tumor which is caused by the growth of the pituitary gland just like acromegaly. The only difference between acromegaly and gigantis is that gigantism is visible in children. The symptoms of gigantism are almost identical to those of acrogemaly.
In children with this disease, excessive height length and early and rapid growth are seen comparing to their peers. Puberty initiates later than their peers. Symptoms of the disease may not be immediately apparent. Especially for children from a family having tall members, it is even more difficult to detect the disease immediately.
Early diagnosis for children is very important to prevent irreversible overgrowth.
Recommendations for acromegaly patients
- You, your family, or your close friends may not notice the symptoms of acromegaly and the changes that occur in your body for a long time. Therefore, if you are not sure of any of the symptoms, consult a specialist doctor immediately.
- Studies have shown that patients with acromegaly may be individuals who are bad tempered, complain about many things, are more demanding and can have more tendency to addiction. On the other hand, they may be too positive. These two extreme mood states may cause you not to give the necessary attention to treatment. This may delay recovery. Do not skip or ignore your treatment.
- If you have been operated, it is very important that you regularly go to your control visits to the doctor. Close follow-up allows you immediately recognize the possible problems and intervene early.
- In some cases, the operation changes your hormone levels but does not cause them return to normal. In such a case, treatment with drugs may need to be continued.
References: 1- Symptoms of acromegaly, 2- Acromegaly, 3- What is acromegaly?