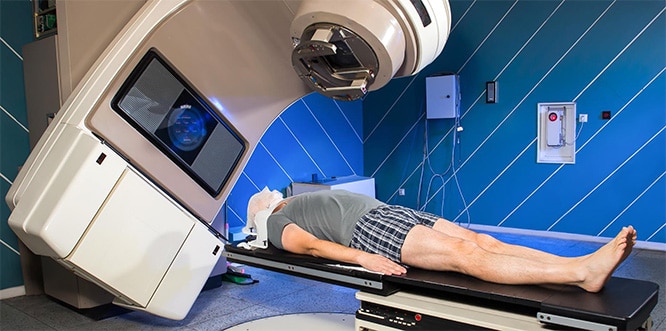
Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) is a treatment that uses radiation to destroy cancer cells with high-energy radioactive rays. X-rays are most commonly used one, but other types of energy, such as protons, can also be used. Nowadays, thanks to the developing computer technology, the target focused machines, the treatment success increases and the side effects are gradually decreasing. Radiotherapy process is in two ways, either externally or internally, but they have similar effects. During treatment, high-energy rays are sent from a machine outside the body. In Brachytherapy, a type of radiation therapy, the radiation source is placed inside the body. Radiotherapy may have various side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, mouth sores, skin problems.
Table of Contents
What is radiation therapy?
Radiotherapy is a type of cancer treatment using high-dose radiation to kill cancer cells and reduce tumors. Low doses of radiation are used for diagnostic purposes, such as x-ray film or computed tomography. Radiotherapy destroys cancer cells, stops them from growing and prevents them from spreading.
Which diseases does radiotherapy treat?
- Brain cancers
- Breast cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Spinal cancers
- Head and neck cancers
- Lung cancer
Types of radiation therapy
There are different types of radiotherapy. Your doctor will determine the most appropriate type of treatment for you. It is usually completed in multiple sessions over a few weeks. External and internal radiotherapy are the most common types.
External radiotherapy
An external machine is used to carefully target cancer cells with radiation beams. The machine is large and can be noisy. During the application, it does not come into contact with the body, it sends radiation beams to a part of the body in many ways. External radiation therapy is a local treatment, it targets at a specific part of the body. For example, if you have cancer in your lung, radiation is applied not to the entire body, but only to your chest.
Internal radiation therapy
The radiation source may be solid or liquid.
- Brachytherapy (Radiotherapy implants): It is internal radiation therapy with a solid radiation source. Inside the body, radioactive implants are placed in small pieces (usually temporarily) near the cancer tissue. Like external radiation therapy, brachytherapy is also a local therapy. It is only for a specific part of the body.
- Radiotherapy injections, capsules or beverages (Radioisotope therapy): Fluid-induced internal radiation therapy is called radioisotope therapy or systemic therapy. Systemic means that the treatment passes to the body tissues through the blood, looks for and kills the cancer cells. It is a method of treatment in which the radioactive fluid or capsule is swallowed or injected into your blood. Along with systemic radiation, radiation continues to spread from body fluids such as urine, sweat and saliva.
- Targeted radionuclide therapy: In this method of treatment, systemically administered radioactive material acts by finding targeted cancer cells.
Process of radiotherapy
Radiation therapists and oncologists work together when applying radiation therapy. An oncologist will decide the dose and type of radiation prior to treatment. The treatment is carried out in several sessions over several weeks. Many people are treated five sessions a week. However, the sessions may vary depending on the stage and type of cancer.
Different types of radiotherapy are applied in different ways:
- In external radiation therapy, a device is used to send X-rays to the body within a certain energy range. There are also devices using other forms of energy, such as electrons, protons, gamma rays, or a combination of these.
- The person who is receiving treatment extends over a table and a technician outside the room runs the machine remotely. An internal telephone is used for communication between the patient and the technician.
- The procedure is usually very short and painless. The patient can return home immediately after the session.
- Internal radiation therapy, called brachytherapy, is performed by non-surgical metal tube, wire or core implants, which can be inserted to the body without any surgery. In some cases, surgery may be needed to place the implant closer to the tumor.
- The duration of stay of the implant is different in each patient. It can go up to the rest of his/her life depending on the patient’s condition.
- The person receiving brachytherapy will have to stay in hospital, because the implants create a radiation risk for other people. Permanent implants release less radiation doses and are considered safe for people around the patient receiving treatment.
How long does the radiotherapy process take?
Radiotherapy is usually performed in a series of sessions with a daily small dose of radiation for 3 to 9 weeks. Before the start of the treatment, your care team will plan the type of radiotherapy you will receive, how many sessions you need, and how often you need treatment. Each session takes approximately 10 minutes.
What should be considered during radiotherapy?
Paying attention to your body health during treatment allows you to be less affected by side effects and to see maximum benefit from treatment. You must follow the advice of your doctor. You can get help from a dietitian for proper nutrition.
Radiation therapy side effects
High-dose radiation is used to destroy cancer cells. Side effects are caused by damage to healthy cells and tissues close to the treated area. However, since new developments in radiotherapy make the target more precise, side effects now have decreased compared to the past. Healthy cell damage due to radiotherapy occurs with many different side effects such as nausea and vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, pain and redness of the skin, wounds in the mouth, hair loss.
How to prevent nausea and vomiting after radiotherapy?
Cancer treatments can cause nausea and vomiting. Controlling nausea and vomiting will help you to feel better and prevent more serious problems such as malnutrition and dehydration.
- You can use anti-emetic drugs called anti-nausea medications.
- Abundant fluid intake will help prevent dehydration.
- Avoid greasy, sweet or spicy food.
- Acupuncture relieves nausea and vomiting in some people. Deep breathing, hypnosis and some other relaxation techniques (such as listening to music, reading books, or meditating) can also help.
Radiotherapy and hair loss
Hair loss is a common side effect in radiotherapy. But unlike chemotherapy, hair loss is limited to the treated area. Hair loss usually occurs 2-3 weeks after treatment. A few weeks after the end of the treatment new hair grows. However, this new hair may sometimes have a slightly different structure or color than before. In high dose radiotherapy, hair loss can be permanent.
Effects of radiotherapy on skin
Some people who receive radiotherapy may experience skin dryness, itching, blistering or peeling. These side effects vary depending on which part of the body is being treated. Skin problems usually disappear after a few weeks of treatment.
Radiotherapy and bleeding problems
If the bone marrow cells are affected after radiotherapy, the number of cells called platelets is reduced. It is a rare condition and usually manifests itself in the form of purple spots under the skin.
Radiotherapy and mouth sores
Head and neck radiotherapy can cause irritation in the mouth and painful wounds called mucositis. The symptoms of mucositis tend to develop within a few weeks after the start of treatment.Your doctor may recommend a pain medication or a special mouthwash. Avoiding spicy, salty or heavy foods can also help. Mucositis usually heals after a few weeks of treatment, but dry mouth may be a long-term problem.
Radiotherapy and weakness
Fatigue is seen in many patients after radiotherapy. This usually begins during treatment and can continue for several weeks or several months after the treatment is finished.
Infections caused by radiotherapy and ways of prevention
Radiotherapy can affect bone marrow producing white blood cells and other blood cells fighting infection. However, since it usually affects only the treated area, the possibility of affecting white blood cells is quite rare compared to chemotherapy. If your white blood cell count decreases too much (neutropenia), your risk of having an infection increases. In order for blood values to return to normal, a short interruption of treatment may be required.
Various infections such as influenza, meningitis, pneumonia and mucositis can be seen after radiotherapy. Adequate and balanced nutrition is important for you to protect from them. Patients should be vaccinated against various infections such as flu, pneumonia, and take vitamin and mineral supplements. Individuals undergoing infection should be avoided, and a mask should be worn when going out.
Diarrhea after radiotherapy
Diarrhea is a common side effect of radiotherapy applied to the abdominal or inguinal region. It usually occurs a few days after the start of treatment. Diarrhea may become more severe as treatment continues. It should disappear after a few weeks of treatment.
How to reduce the side effects of radiotherapy?
- Stay away from alcohol and smoking.
- Follow the nutritional recommendations below.
- Use vitamins and minerals if your doctor recommends.
- Regularly brush your teeth and gargle daily to reduce mouth and tooth problems.
- Do not rub or scratch your skin.
- Choose soft, cotton and loose clothing.
- Protect your skin from the sun.
- Clean your skin with warm water and soap every day.
- Bath with lukewarm water, avoid using scrub and fiber.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Stay away from people undergoing infections.
- Use the recommended remedies for nausea and vomiting.
- Try to relax with meditation, relaxation exercises, breathing techniques.
- Try complementary medicine methods such as acupuncture.
Nutrition before and after radiotherapy
- Consume at least 2 liters of fluid per day
- Apply a healthy diet program under the control of a dietician.
- Eat foods that meet the protein requirement until side effects occur. Eat at least one egg every day and have protein-rich meal and chicken broth soups.
- Try to consume food in as much liquid form as possible.
- Avoid spicy and acidic foods that may irritate the mouth and throat.
- Stay away from very cold or hot food and beverages.
- Stay away from sugary foods.
Sexuality and pregnancy during radiotherapy
Radiotherapy can cause various sexual and fertility-related side effects in men and women. For men, side effects often occur after radiation therapy to the prostate and testes. Erectile dysfunction, low sperm count and activity are possible side effects. The following side effects may be seen in radiation treatments applied to the reproductive organs in women:
- Changes in menstruation
- Interruption in menstruation
- Early menopausal symptoms such as itching, burning and dryness in the vagina
- Infertility: It can occur especially when radiotherapy is applied to both ovaries.
Radiotherapy, drug interactions and alternative medicine
Evidence suggests that some agents such as certain dietary supplements and preservatives have antioxidant properties and hence inhibit the effectiveness of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. So, it is important to inform your doctor about any drugs, supplements and herbal methods that you use before radiotherapy.
Recommendations for patients receiving radiotherapy
- Before you start radiotherapy, you should always tell your doctor about all the drugs, vitamins and herbal supplements you use to avoid possible drug interactions.
- You may feel very tired during and after radiotherapy. Get plenty of rest.
- Try to consume foods rich in protein and calories.
- Treat your skin in the area where you receive radiotherapy. Clean your affected skin area with warm water and the soap (recommended by your doctor) every day.
- Stay away from crowded environments. When going out, wear masks in order to protect yourself against infectious diseases during the treatment period.
- To minimize the side effects of radiotherapy to the digestive system, start a healthy diet and get information from a dietitian. For more:>>> Radiation therapy